AWS vs. Azure vs. GCP: A Comparison of Cloud Platforms
Contents
Cloud computing refers to the practice of accessing computing resources and power on demand, without the need for active management by the user. These resources are typically distributed across multiple locations, known as data centers, and are accessed through a “pay-as-you-go” model that is based on resource sharing.
The use of cloud computing services has been on the rise in recent years, with more and more companies and organizations using the cloud to access IT systems and software resources. With cloud services, companies can increase their efficiency by having rapid and continuous access to databases, analytics, and software, which can help them to develop and grow their business.
The most dependable, flexible, and secure cloud computing services are offered to the general public by Amazon, Microsoft, and Google. While there may be differences, the three services have similar characteristics. While there may be differences, the three services have similar characteristics. So, in this post, we will enlighten our readers and those looking for a GCP vs Azure vs AWS distinction. We will discuss the solutions, tools, pricing, security policies, and some other aspects these three cloud computing platforms have to offer.
Azure vs. AWS vs. GCP: an Overview
Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform, and Amazon Web Services have been the top three cloud providers in the market for the last couple of years, as of 2023 research. They keep providing excellent networking, computing, and storage services to a wide range of sectors worldwide. In this section, we’ll be comparing AWS, Azure, and GCP in terms of the companies’ positions in the global market.
Worldwide Revenues
AWS, an Amazon subsidiary for over 20 years in the market and the highest revenue in the industry, offers metered pay-as-you-go, on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, continuously taking a third of the worldwide revenue.
Azure, operated by Microsoft since 2008, offers similar services via the Wide World Web, is the second most profitable in the market and gradually becoming a major competitor for AWS. It helps companies and individuals by building, running, and managing software apps and tools across different clouds.
GCP, considered the youngest in the Google Cloud vs AWS vs Azure contrast, was launched the same year as Azure but has been actually generally available only since 2011. It provides a robust assemblage of cloud services that can run and support any application.
Market Size
The market for cloud computing has been expanding quickly in recent years and is predicted to grow further in the years to come. A report from Grand View Research states that with a forecasted compound annual growth rate (CAGR) OF 14.1 from 2023 to 2030, the global cloud computing market, which was estimated at USD 483.98 billion in 2022, will develop at a faster pace than average.
Pay-as-you-go SaaS-based business models and the functional ability of cloud computing to improve business performance are some of the major factors that are anticipated to fuel this market growth.
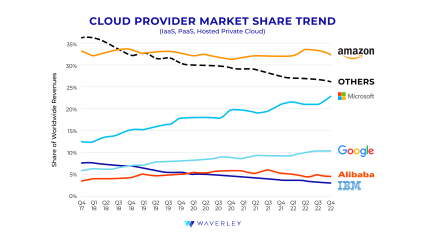
According to Statista, the cloud platforms that make up the global share market for cloud computing services are Amazon (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, and IBM Cloud. Among all of these, there are three platforms that make up most of the market and the subject of this article.
Thus, in terms of this cloud platform comparison, at the top, with the highest market share, there is AWS, which has been controlling about 32% of the industry for the couple last years. Microsoft Azure takes the second place in the leading board with over 23% of the market share. Lastly, GCP, among the three, comes in third with just under 10%, so far. Altogether, they account for 65% – almost two-thirds – of the total cloud computing market share.
Global Infrastructure
Cloud providers deliver their services over the high-bandwidth global fiber network that spans across oceans and continents. This network connects multiple physical data centers housing the servers that provide storage and computing capacity to cloud services users. A set of data centers that are interconnected through a dedicated low-latency network and deployed within a certain latency-defined perimeter make up a region. Each region falls under a specific pricing and service availability offering.
Within a service region, cloud providers distinguish physically separated availability zones consisting of one to several data centers that guarantee the availability of users’ data and services in case of unforeseen failures. Another part of the global cloud infrastructure are the Points of Presence (PoPs) – physical locations and access points at the edge or intersection of networks that ensure network accessibility, performance, and redundancy for the optimal delivery of cloud services, including edge locations and data centers.
In the table below, we summarize the numbers that reflect the AWS vs Azure vs GCP comparison of infrastructures.
| Countries | AvailabilityZones | Regions | Edge Locations | Points of Presence | Data Centers | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AWS | 245 | 102 | 32 | 400+ | 600+ | 100 |
| Azure | 140* | 180** | 60 | 192 | 185+ | 300+ |
| GCP | 200+ | 118 | 39 | 187 | – | 24 |
*as of 2020, no current data
** three Availability Zones per supported Azure region
– no current data
Amazon Web Services currently cover 102 Availability Zones in 32 Geographic Regions across the Americas, Africa, Europe, Middle East, Asia, and Oceania, promising to further expand. This includes 245 countries and territories, which is also the highest number of served areas in the Azure, AWS, and Google comparison.
Azure provides its services in more than 60 Azure regions around the globe that comprise over 300 physical data centers, and over 185 points of presence, compared with Amazon’s 600. As of January 2020, Amazon was known to have a presence in 140 countries around the world.
Google Cloud Platform claims availability in more than 200 countries and territories and is actively expanding its network. GCP offers its coverage in 39 regions and 118 zones, almost every region including three zones.
AWS vs Azure vs GCP: Service Competition
The range of services each of the three major cloud vendors provides is continuously expanding to keep up with the competitors and be the first to deliver innovation to their users. This includes such trending solutions as low-code and AI-assisted coding, generative AI models, machine learning, automation, big data analytics, edge and serverless computing, all reducing the price to help customers optimize their costs.
Among other tools used in cloud development services, AWS, Azure, and GCP provide a choice of compute and storage services, including database options that integrate a wide range of technologies to accelerate development. Integration services are essentially useful in cloud computing as they are a system of tools and technologies that place together different applications, systems, repositories, and other cloud development services.
Cloud Service Models
Before we move on to discussing the service offerings from AWS, Azure, and GCP, here’s a quick reminder about the cloud service delivery models for our readers:
- Software as a Service (SaaS) is a software licensing model that allows users to access the software on a subscription basis using external servers. Typically, SaaS products are ready-to-use, intuitive, user-facing applications with no or relatively low learning curve, fully managed by the provider.Examples of cloud SaaS offerings include Amazon WorkMail, Microsoft’s Office 365, and Outlook or Google Workspace and Google Drive.
- Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model that provides a complete cloud platform – hardware, software tooling, and infrastructure – for users to develop, run, and manage applications without the cost, flexibility issues, and complexity of maintaining such a platform themselves. The PaaS userbase will be software developers with the skills and knowledge required to use the tooling to create software applications.
Some examples of PaaS are AWS Lambda, Azure Service Bus, or Google’s Cloud Run and App Engine. - Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that provides clients with the needed IT infrastructure, such as computing, storage, and networking on demand, usually on a pay-per-use basis. Under this service provision model, the cloud provider manages the infrastructure while the user, usually a company with plenty of resources, remains responsible for handling the deploying, maintaining, and supporting of their apps.
Amazon EC2, Azure Virtual Machines, and Google Compute Engine are some of the most prominent examples of IaaS offerings from the top three cloud providers.
All of the cloud service providers in question try to stay innovative and competitive, continuously rolling out new offers and services complementing their existing stack. So, questions like “AWS vs Azure vs GCP, which is better” may arise. To answer that, further we discuss the Azure vs Google vs Amazon service offerings and find out the strengths and weaknesses of each cloud provider.
Cloud Computing Services
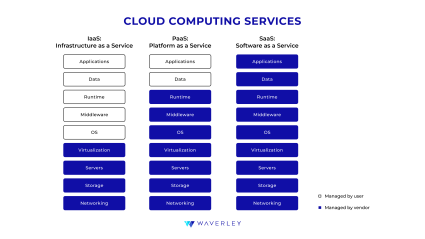
A variety of popular computing services, such as virtual machines, containers, and serverless computing, are provided by all of The Big Three cloud providers. Recognized as Gartner Magic Quadrant Leader for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform Services for twelve years in a row, AWS offers the broadest range of cloud computing choices, with a selection of instance types and sizes. Similar services are provided by Azure, which is more well-liked by companies that use Microsoft’s products due to its smooth integration. Kubernetes and other open-source technologies are well supported by GCP, which is renowned for its user-friendly UI.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Workloads
All three companies offer many AI and ML services for application development, including speech recognition, speech synthesis, natural language processing, computer vision, data extraction, and more. Amazon’s SageMaker and Rekognition are only two of the many AI and ML application development services that AWS provides. Azure offers comparable services, such as Azure Machine Learning and Cognitive Services. Cloud AI Platform and Cloud Vision API are two of the AI and ML services provided by GCP.
Generative AI
With the arrival of OpenAI’s ChatGPT, generative AI has become a must-have technology in many modern solutions. To satisfy clients’ needs in this domain, AWS offers Amazon Bedrock – a service providing access to multiple Fully Managed Models for creating apps with text and image generation functionality avoiding the need to take care of infrastructure management. At their last event, they also presented AmazonQ – a generative AI-powered assistant, and PartyRock – a sharable playground for Amazon Bedrock.
Azure has certainly benefited from OpenAI’s pioneering in this market, serving as OpenAI’s exclusive cloud provider with its Azure OpenAI Service. GCP is not falling far behind, having rolled out the enterprise-ready Vertex AI technology for work with Large Language Models (LLMs).
Below, you can find the comparison of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offerings arranged into a table, taking into consideration pricing and the most popular services, such as integration services, storage, networking, security, and developer tools.
| Service Competition | AWS | AZURE | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pricing |
|
|
|
| Integration Services and Features | Allows easy integration using Amazon EC2. | Allows integration using Azure VM, Azure App Service, SQL databases, and more. | Allows service integration for Compute Engine using Cloud Storage services, Cloud SQL, and more. |
|
|
| |
| Cloud Storage Technologies | Storage Services:
| Storage Services:
| Storage Services:
|
Databases:
| Databases:
| Databases:
| |
Database Solutions:
| Database Solutions:
| Database Solutions:
| |
| Developer Tools |
|
| Cloud Tools:
|
| Networking | Amazon Virtual Private Cloud – VPC
| Azure Virtual Network – VNET
| Cloud Virtual Network
|
| Cloud Security & Compliance |
|
|
|
This AWS, GCP, and Azure comparison shows that all three provide an extensive range of cloud-based services that their customers can benefit from. Most of them have decent alternatives across different platforms. But one should remember that in some cases, certain services may not be available depending on the country or region, so stay alert for location-specific offerings of cloud providers and pick the one that will definitely be closer to your users.
In the following section, we’ll proceed with the Azure, AWS, and Google comparison, concentrating on each cloud provider’s strong and weak sides.
Amazon Web Services (AWS)
AWS is considered to be the leading cloud service provider globally, claiming more than 30% of the market share and offering the most extensive range of developer tools and solutions (over 200 services) for cloud development. Nevertheless, we can find both pros and cons of AWS, as compared to its main competitors.
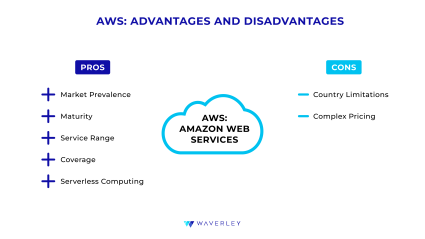
Pros of AWS
- Market Prevalence
As we’ve outlined previously, AWS has been there for a longer time and has gained one-third of the global cloud services market. This makes it a more experienced and confident player with a well-built brand name, extensive infrastructure worldwide, and a quantitative advantage over the competitors. - Maturity
Of the three cloud providers in question, AWS has been in the cloud solutions market for the longest and has an established reputation. This also means it’s infrastructure and services are time-tested and reliable while its business partnerships can last for decades. - Service Range
Currently, Amazon Web Services can provide its users with over 200 solutions and services for storage, networking, data analytics, cloud computing, and cloud-native development. This includes service offerings for low-latency solutions, on-premises applications, public sector and highly regulated domains, and even satellite communications. - Coverage
AWS claims to have the largest cloud infrastructure among cloud service providers, with the most data centers and PoSs around the globe. They are also known to have the largest amount of hyperscale data centers. An extensive infrastructure allows to deploy your AWS cloud apps as close to your users as possible, delivering high performance and minimal latency. - Serverless Computing
While all three cloud service providers offer multiple tools for serverless computing, AWS Lambda remains the top choice of software engineers as the most established and mature technology. It is also preferred for its flexible pricing, wide language adoption, and auto-scaling based on workload changes.
Cons of AWS
- Country Limitations
AWS is limited to certain countries. Since Amazon is based in the United States, each service promoted may not be accessible or limited by default in certain countries. - Complex Pricing
A rather general problem, with flexible and pay-per-need billing models, comes the complexity of keeping track of all the resources actually used, which gets even harder with regional discrepancies.
However, such drawbacks can be easily mitigated with the support and guidance of qualified specialists providing AWS consulting services.
Among the companies that use AWS based on EC2, there are giants that spend between $8 to $20 million in monthly expenses:
- Netflix
- ESPN
Microsoft Azure
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform with a huge focus on enterprise clients and smooth integration of its cloud services with the entire Microsoft ecosystem. With Microsoft’s OpenAI debut in the generative AI arena, Azure has gained a great advantage over the competitors in this field and is working on innovation to keep their standards high. Same as AWS and GCP, Azure has its advantages as well as some disadvantages that existing and potential Azure cloud consulting companies should consider.
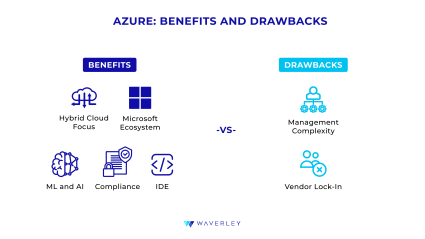
Pros of Azure
- Hybrid Cloud Focus
Unlike AWS and GCP, Azure is known to pay a lot of attention to supporting hybrid cloud environments. This is particularly beneficial for customers from highly regulated domains who need to keep some part of their infrastructure on-premises. Potential cloud users willing to migrate from on-prem gradually will also appreciate high-quality hybrid cloud services. - Microsoft Ecosystem
As we’ve already mentioned, Azure Cloud provides its clients with smooth integration with other Microsoft solutions and services, which makes your entire infrastructure manageable with a single Microsoft account. This particularly appeals to large enterprise customers with established business relationships with the company. - ML and AI
Azure is the exclusive OpenAI partner providing access to the Azure OpenAI Service for its customers. Azure’s ML services also include a complete toolset for building AI-powered solutions, from low-code to advanced developer tooling. And of course, we cannot avoid mentioning GitHub Copilot developed in collaboration with OpenAI – the pioneer generative AI-powered coding assistant which has been around for a while. - Compliance
Azure is often the top choice for heavily regulated domains not only because its attention to customers with on-premise infrastructure. It also has a broad range of compliance certifications, meeting the regulatory requirements of various industries. - IDE
Microsoft’s Visual Studio is known to be many software engineers’ favorite for the support of multiple programming languages and extensive functionality that allows one to complete an entire SDLC in one place. It is also integrated with Azure’s ML development toolset, providing even more flexibility and creative opportunities.
Cons of Azure
- Management Complexity
As with any large-scale solution, Azure infrastructure requires specialized management and upkeep, including full-time resource monitoring and optimization. Therefore, it is essential to get proper expertise, in-house or outsourced at a digital transformation company, to handle the platform’s infrastructure efficiently. - Vendor Lock-In
A benefit for businesses whose needs can be fully satisfied by Microsoft’s ecosystem, this turns into a stumbling stone if you come to realize that other provider’s tools or services will work better in your scenario. You might consider going for a multi-cloud strategy to avoid such a situation.
Azure is most often chosen by large-scale products and companies. Here are some of the companies that rely on Azure’s cloud infrastructure:
- Shell
- eBay
- Johnson & Johnson
- Honeywell
- Dell
Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
GCP is a public cloud vendor that also offers a range of cloud computing services where users can handle their Google Cloud projects. GCP is among the best Cloud service providers, yet there are both noticeable advantages and drawbacks.
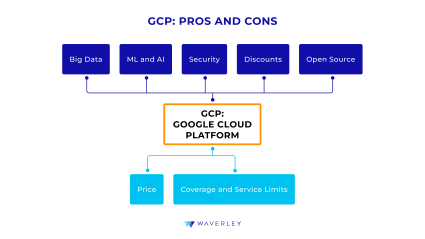
Pros of GCP
- Big Data Processing
Google has a long-standing experience in processing big data gaining valuable insights from it based on a variety of variables, including search history, location tracking, user behavior tracking, etc. Given that big data is one of GCP’s main strong fields of expertise, it has a variety of cutting-edge tools for cloud warehousing as well. - ML and AI
The creator of the Text-to-Speech and Speech-to-Text solutions that were the first of their kind, GCP is particularly strong and experienced in the field of natural language processing, voice recognition, and image recognition and continues to deepen this expertise. - Robust Security
GCP is known to pay great attention to physical and informational security for their users’ applications with a range of backup, security, and identity services, including Identity and Access Management (IAM), Security Command Center, Confidential Computing, and Key Management Service. It also ensures compliance with industry standards and certifications. - Discounts
If you use GCP’s per-minute billing offer for computing in conjunction with the Sustained Use Discount, it can be more cost-effective than other providers’ services. It will also be the cheapest of the three when using general-purpose instances and when it comes to monthly charges for a Linux server. - Focus on Open Source
As a cloud services provider, GCP takes extra steps to ensure the platform’s compatibility with open-source tools and solutions. This gives software developers more freedom in choosing their development kit and lets them experiment and play with technology freely, relying on Google’s platform.
Cons of GCP
- Price
Although the cost of using GCP is mentioned as a benefit it can also turn out to be costly. It has the highest prices for compute-optimized, memory-optimized, and accelerated computing instances among the Big Three. However, the discount rate for a year and longer commitment will provide a discount at the highest rate as well. So count well before you choose. - Coverage and Service Range
Compared to its two rivals, GCP has the least developed global infrastructure and the shortest service range, even though it has an advantage in some service domains, such as Big Data or Machine Learning. However, now GCP is rapidly gaining traction, bringing it much closer to AWS and Azure with time.
Among the top global companies that prefer Google Cloud Platform as their cloud infrastructure vendor are the following:
- Paypal
- Home Depot
- UPS
- Cardinal Health
To compare GCP, AWS, and Azure, we took into account the benefits and drawbacks each of them has, whether different or similar.
An Overview of Comparisons
All three major cloud computing service providers have developed strong cloud infrastructure networks over the years. With certain differences in coverage and feature sets, they are regarded as the finest options in the market. Thus, it is mostly the GCP vs AWS vs Azure question when it comes to pricing and services range to choose from on a case-by-case basis.
All things considered, we can make a general conclusion as to what kind of projects each of the cloud service platforms can be best suited for, with many of them overlapping or having good alternatives on the competitors’ platforms.
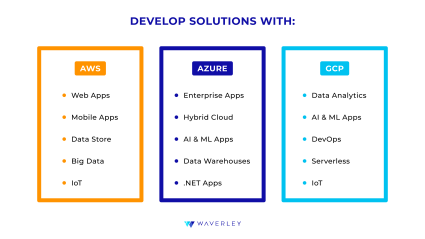
AWS is Best For
- Web application development with such services as Amazon EC2 instances, Amazon S3 for storage, AWS Elastic Load Balancing solution, and AWS CloudFront as a leading service for content delivery.
- Mobile application development using AWS Mobile Hub, AWS AppSync, Amazon Cognito, as well as AWS Lambda and AWS Amplify that are great for mobile backend development.
- Data storage solutions with Amazon S3 service for object storage, Amazon EBS for block storage, and Amazon Glacier for long-term archival. It also offers solutions for different database types with Amazon RDS, DynamoDB, and Amazon Redshift.
- Big Data and BI solutions using Amazon EMR for big data processing, Amazon Athena for ad-hoc query analysis, Amazon Kinesis for real-time streaming data processing, and Amazon QuickSight for business intelligence and analytics.
- IoT and Connected Devices development with AWS IoT Core and AWS IoT Analytics for collection, storage, and analysis of data from IoT devices.
Read our AWS IoT + Cognito: IoT Devices and User Management Solution blog article to learn more about Waverley’s IoT development expertise with the AWS toolset.
Azure is Best For
- Enterprise Application Development with broad tooling for building, deploying, and scaling, including such tool as Azure Logic Apps designed to create workflows for smooth application integration.
- Hybrid Cloud Solutions using Azure Arc to easily manage your resources across on-premises, multi-cloud, and edge environments.
- AI and ML Solutions with Azure Machine Learning for building and deploying ML models, Azure Cognitive Services for pre-built AI capabilities, and Azure Bot Services for building intelligent bots. Don’t forget about the opportunities Azure provides for generative AI solutions due to integration with OpenAI – read our guide on how to integrate ChatGPT into your business.
- Data Warehousing Solutions with the Azure Synapse Analytics service.
- Windows Server and .NET Applications working best with the Azure infrastructure and its Azure Virtual Machines, Azure DevOps, and Visual Studio Team Services as their preferred choice.
To learn why you might want to choose .NET for application development, check out our Pros and Cons of .NET Development blog article.
GCP is Best For
- Data Analytics Solutions using such Google services as BigQuery for real-time analytics, Cloud Dataflow for stream and batch processing, and Dataprep for data cleaning and transformation.
- ML and AI Solutions with the AI Platform, AutoML, and TensorFlow services from Google for supreme development, training, and deployment of a variety of machine learning models.
- DevOps and Container Orchestration with the leader in this domain – Kubernetes, originally developed by Google.
Serverless Computing with Google App Engine and Cloud Functions that greatly facilitate serverless architecture development. - IoT Solutions with Cloud IoT Core for device management and Cloud Pub/Sub for event-driven computing that ensure connection security and scalability.
In our Introduction to Google IoT Cloud for IoT Projects, you can find a detailed guide on using this tool for your future IoT product.
How to Choose a Cloud Service Provider
If you are still hesitating about the benefits of moving to the cloud in general, we recommend reading our blog article on the 10 Reasons Why You Should Migrate to the Cloud. But if you’ve made up your mind on that already, the time has come to understand which provider fits your business best.
Understanding Your Business Needs
To better understand your business needs in cloud resources, try to put down as much information about your project as possible. These questions might be helpful:
- What are my short-term and long-term objectives for using the cloud?
- What resources exactly do I need and how much (e.g. storage, database, compute capacity)?
- What is my users’ geography?
- What are my load, scalability, and performance requirements?
- Am I looking for low-code or pro-code solutions?
- What cloud services will I need for my application architecture?
- Do I need any integrations?
- Does my application fall under certain compliance regulations?
- What can be my security concerns?
- What are my budget limits?
- Who should be responsible for managing and supporting my infrastructure and resources?
- How can I measure my cloud’s infrastructure efficiency?
Finding Your Match
Having a clear picture of your needs and capabilities, you now can get down to researching what cloud service providers have to offer. To choose the cloud service provider that will be right for your business, we recommend paying attention to several key factors, namely:
- The provider’s credentials and quality standards.
- Cloud security options you can make use of
- Industry compliance guarantees for your product
- Solution manageability
- Architecture and integration needs
- Service levels you need
- Support provided
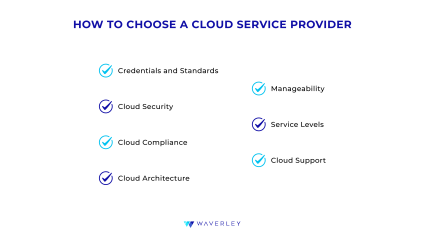
- Credentials and Standards
High service quality should be a major concern if you want to develop a reliable software application and avoid wasting your resources. Thus, adherence to industry best practices is a key factor that can determine the choice of the cloud service provider. Taking standards into consideration first should help narrow down the pool of prospective suppliers, while credentials and reviews will add more credibility and certainty. - Cloud Security
If your application will be handling any sensitive information, data security measures must be your top priority. Carefully study each provider’s physical and informational security measures they take, what backup options they provide, and how they mitigate breaches and unforeseen events. Find out the service range the providers offer to meet their clients’ security needs. - Cloud compliance
For digital solutions for highly regulated domains, choose a cloud platform that can meet the compliance standards specific to your industry and business. Find out which cloud provider (s) can ensure compliance within your industry. Once you’ve put your applications and data on cloud infrastructure, understand what it takes to stay compliant. Make sure you understand where your responsibilities lie and what compliance issues your vendor can help you with. - Architecture
Depending on whether you have an existing system or not, draw your application’s architecture design taking into account integration with all your workflows, current and future. For example, if you’ve already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem, opting for Azure may make sense. Additionally, consider your cloud storage architecture. Microsoft, Amazon, and Google all offer multiple types of storage meeting different needs, but the types of archival storage are different. If it matters, make sure you understand the subtle differences between them. - Manageability
Define the level of expertise needed to manage your cloud infrastructure and research what cloud service providers can offer to meet your capabilities. If it turns out that you’ll need to hire a certified cloud expert, consider service options that include infrastructure and resource management on the provider’s part. However, be ready to pay more and have to do with less flexibility and customization opportunities. - Service levels
Service levels are important if your organization has stringent requirements for availability, response time, capacity, and support. A cloud service level agreement will be your main guide (cloud SLA) when choosing a provider. It’s essential to establish a clear, legally binding contractual relationship between the cloud customer and the cloud provider. Pay particular attention to legal requirements regarding the security of data hosted on cloud services, especially regarding compliance provisions. - Support
Another critical factor to consider is support. If you need help, will you get it quickly and easily? Some cloud providers only offer support through a chat service or call center, which may not be acceptable for your needs. Others may offer dedicated resources, but they may have limited time and access. Make sure you inquire about the level and type of support you can access.
AWS vs. Azure vs. GCP: Conclusion
In this blog article, we tried to provide an extensive Azure vs AWS vs Google Cloud comparison to help users interested in these services make a well-weighed decision based on expert knowledge.
Currently, AWS takes the lead by having the most well-developed global infrastructure in the market of cloud computing services. Meanwhile, Azure and GCP are doing their best to stay competitive and attract more users by actively growing their global networks and keeping up with (or even pioneering in) technology innovations. Therefore, predicting which of the three may become a market leader within the next few years is difficult.
We made some general assumptions that AWS can be the optimal choice for web and mobile development as well as database and storage solutions, Azure is great for enterprise-level solutions and integration with Microsoft’s services, while GCP’s strengths are big data and AI-powered solutions. However, this does not exclude other providers from delivering decent alternatives.
From pricing models to services comparison, the AWS vs GCP vs Azure contrast reveals that each one has both strong and weak points and there is no way we can clearly say which one is the best cloud service provider. This is to be decided on a case-by-case basis, depending on the business needs.
We hope this article helped you answer some of your questions about the AWS, Azure, and GCP differences. If you need a more in-depth consultation on cloud computing services for your business case, Waverley experts are ready to help. Please, use the form below to contact the Waverley team and we’ll get in touch with you.
FAQ
Which is better: GCP, AWS, or Azure?
AWS is undoubtedly considered as the most advanced and developed cloud provider of the three. However, Azure and GCP are quickly meeting high expectations for different companies. Therefore, if you want to know which of these is the best-suited platform for you, the ultimate answer is that the winning platform will be the one that meets your expectations and needs depending on the services you may require.
Who is AWS’s biggest competitor?
As mentioned at the beginning of the Article, AWS comes in the first place place followed by Microsoft Azure and then GCP. Therefore, if needed to compare Azure and GCP, Microsoft takes the lead becoming Amazon Web Services’ biggest competitor.
What is the difference between AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure?
As there are similarities between AWS, Google Cloud, and Azure, there are differences in many aspects as well. First of all, despite similar business models, all three cloud service providers offer different pricing schemes that include various service levels, rates, and discounts.
More importantly, depending on each one’s strong areas of expertise, their service range and depth would differ from one domain to another. For example, AWS clients will greatly benefit from an extensive infrastructure for broad or location-specific app user geography, Azure will make a perfect fit for existing Microsoft clients or those looking for a hybrid cloud, while GCP will be of help in big data processing and ML workloads.
Which is better for startups, Google Cloud, AWS, or Azure?
Either platform can work for startup companies, each having special startup programs to offer. However, the service used and the success of the same will depend on what the startup needs. AWS, Azure, or GCP are good options bor for startups and well-established companies considering the type of service and which feature fits their business best.
Which cloud platform is the cheapest?
Taking into account the AWS, Azure, and GCP service comparison, the pricing schemes, and respective discount rates, all three will end up having competitive fees for businesses. On the other hand, a lot depends on the cloud infrastructure and services you’ll need as well as your region – what’s cheaper in one case, can be more expensive in another. For their prospects to be able to roughly compare their potential expenses based on their individual needs, each cloud vendor provides a price calculator on their website.
Transform your business in the cloud.