10 Reasons Why You Should Migrate to the Cloud

Contents
Why move from on-premise to the cloud? The global pandemic as well as the ubiquitous implementation of the Big Data, AI, and ML technologies that require enormous computing capabilities and storage have urged businesses to consider end-to-end digital transformation with cloud computing. The latest research shows that the global cloud market is expected to grow from $677.95 billion in 2023 to $2,432.87 billion by 2030, which is more than by 350%!
To help you understand why companies decide to move to the cloud, we explain what cloud computing is, share the benefits of moving to the cloud, describe the process to follow when moving to a cloud computing platform, and analyze cloud expenses and pricing.
What is Cloud Computing?
The term “cloud computing” is considered to be the supply of various computer services via the internet. It works using a network of remote servers accessed through the internet instead of relying on local servers or individual devices for data processing and storage. To start using cloud computing, one has to complete the process of cloud migration which is moving digital assets, such as applications, data and other IT resources, from the on-premises to a cloud-based infrastructure. With a variety of cloud consulting services available nowadays, business owners can leverage the full potential of the cloud technology.
Cloud Computing Types
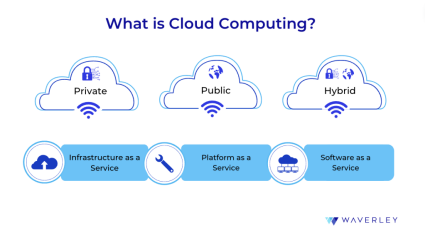
In terms of infrastructure deployment models, there is a variety of ways a business can embrace cloud computing. They differ depending on the range of services that need to be used, domain-specific security and privacy requirements, and pricing. Thus, cloud adopters may choose among the private, public, or hybrid cloud deployment models.
- Public Cloud
Public cloud provides access to a variety of computing services, such as virtual computers, storage, databases, as well as top modern solutions for Business Analytics, Big Data, Artificial Intelligence, and Machine Learning. As one of the great reasons to migrate to the cloud, this option lets you benefit from high levels of scalability and cost-efficiency, enabling your business to grow. - Private Cloud
Choosing private cloud, you own the hardware infrastructure that your system runs on or get a vendor’s private cloud server at your disposal that lets you increase your data privacy. For example, if a business is required to meet strict regulations and compliance requirements, public cloud will provide more control over your data and resources. Also, despite high initial investment, the total cost of private cloud long-term can turn out favorable. - Hybrid Cloud
This deployment model combines the best of both worlds: the limitless scalability of the public cloud and the control and security levels of the private cloud. With a bit of each, you can distribute your workloads in the most optimized way between your private and public resources. Hybrid cloud can also easily integrate the on-premises resources you might already have and want to make use of.
Cloud Computing Services
Today, cloud computing vendors offer multiple services that help customers cover a wide range of needs, from the infrastructure, computing power, and tools to create own software from scratch to having the ready-to-use solutions at their fingertips. Thus, the cloud service market is typically divided into three primary service models or segments, encompassing infrastructure, platforms, and software.
- Infrastructure-as-a-Service
Under this service type, you pay for using the vendor’s computing resources, such as storage, servers, network, and virtual machines to run your system on them. This way, you don’t need to bother about purchasing, managing, and supporting your own hardware as IaaS provides your business with the freedom to scale your infrastructure up or down as necessary. Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Engine are the most common examples of the IaaS products. - Platform as a Service
PaaS is typically created for developers to provide them with tools and resources, so they can create, test, and deploy apps without having to worry about the underlying technology. AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Azure Cognitive Search, or Google App Engine are all examples of cloud tools that work as PaaS. If you are fine with having less flexibility or freedom of choice in terms of technologies and want to avoid the complexity of setting up, configuring, and managing the infrastructure, servers, storage, networks, and so on, PaaS is the service type you might prefer. - Software as a Service
SaaS has now become the most common software delivery model. With SaaS, users only need a browser and internet connection to use any of such apps. Business owners don’t need to manage or oversee any underlying infrastructure and, oftentimes, do any development, as SaaS is a ready-to-use product. Enterprise-level SaaS solutions are more cost-efficient and rapidly deployed and offer a certain degree of customization. Just think of Salesforce, Google Workspace, or Dropbox to have an idea of what SaaS is.
10 Advantages of Moving to the Cloud
Now that you have a clear idea of what cloud computing is, let’s discuss why move to the cloud at all. In fact, there can be reasons to move to the cloud specific to every individual type of business. However, cloud migration benefits are also evident for any company’s workflows and software ecosystem in terms of the ease of support and maintenance. Also, on-premise infrastructure stays behind if compared to the potential cost reductions and scalability provided by the cloud.
In this section, we take a closer look at what are the benefits of moving to the cloud.
1. Cost Savings
Among the many reasons to migrate to the cloud, you can find that cost savings is an essential one. By using cloud computing, you can access processing and storage capabilities for less money because you won’t have to make significant upfront hardware and infrastructure investments. This reduces the cost of maintenance, upgrades, and physical storage as these responsibilities pass to the cloud service providers. Additionally, you can use the available resources based on your actual needs as cloud service providers offer pay-as-you-go pricing options.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
You can manage your resources with unequaled flexibility and effectiveness by moving to the cloud. The cloud allows you to quickly scale resources up or down in response to your business needs, providing you the freedom to change your processing power, storage, and network capacity on demand. Having avoided the lengthy setup and purchase procedures associated with the conventional IT infrastructure, you won’t wonder why move to the cloud as it will ensure quick and simple resource provisioning for you.
3. Improved Performance and Reliability
In the event of a hardware failure or other disturbances, cloud service providers frequently offer a robust and supplementary architecture to guarantee service availability. Geographically dispersed data centers further lessen the possibility of single points of failure and improve the system’s overall resilience. By giving you simple access to resources and data from any place with an internet connection, switching to the cloud has further advantages for you.
4. Enhanced Security
Cloud vendors are always thinking ahead and aim to secure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their customers’ data as much as possible. They widely apply such techniques as data encryption, identity management, access controls, cloud firewalls, and powerful threat monitoring tools. At the same time, cloud migration cannot be a silver bullet for security threats lurking for your weak spots. Thus, proper cloud security configurations, a consistent security policy within your organization, a backup and business continuity plan in place as well as regular employee trainings will only help you strengthen your cloud infrastructure against known software vulnerabilities and breaches.
5. Increased Collaboration and Accessibility
Moving to the cloud allows your teams to work together in real-time, regardless of where they are physically located, removing obstacles and fostering effective communication and cooperation. Additionally, cloud computing helps boost productivity and flexibility by enabling users to access data and apps from a variety of devices. Your staff may easily connect to the cloud and use resources from a laptop, tablet, or smartphone wherever they are.
6. Streamlined IT Operations
If you are looking to move to the cloud, you can start by giving the cloud provider control over managing your infrastructure. This way, you can avoid spending a lot of time and money on upkeep and administration of your own equipment. This shift of accountability results in a lighter load for everyday operations such as maintenance, updates, and patches, allowing IT staff to focus on more strategic objectives. What’s more, cloud vendors offer a multitude of tools and services that automate the cloud infrastructure management process.
7. Innovation and Agility
The transition from on premise to the cloud gives you access to a wide variety of cloud services, enabling you to explore and test new ideas in a scalable and adaptable environment. Your apps and other services can be developed and released more swiftly. You also get to make use of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning by utilizing cloud computing.
8. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Cloud-based solutions offer robust automated backups and alternatives for disaster recovery, significantly enhancing your business’ resilience. In the case of an unforeseen occurrence, these procedures allow you to restore data, reduce the risk of data loss, and avoid downtime. Additionally, cloud-based backup and recovery solutions facilitate faster recovery times, enabling you to quickly restore operations and keep your business continuity.
9. Compliance
With the cloud, it’s much easier to meet the regulatory and compliance requirements across industries. Especially when specialized software software products are in great demand by highly regulated industries, such as finance, healthcare, and government. Waverley is now actively working on such projects in the healthcare and energy domains, for example. Additionally, utilizing the cloud capabilities, you streamline processes, show your dedication to upholding the highest standards of data governance, and successfully traverse the difficult world of regulatory compliance.
10. Environmental Sustainability
Among the reasons to migrate to the cloud you will find that it helps the environment. The possibility of lowering your organization’s carbon footprint is one important benefit. Cloud services reduce the environmental effects caused by conventional on-premises infrastructure by pooling resources and improving energy efficiency. Additionally, data centers, the foundation of cloud computing, are adopting more environmentally friendly procedures. This induces switching to renewable energy sources to run their businesses, further lowering their dependency on fossil fuels.
Getting Started with the Cloud
Cloud computing gives firms the chance to decentralize the ownership of their hardware and software, which will ease their technology operations. The key to a successful transition from on-premise to the cloud is a well-organized process that accounts for every part of your system. Thus, in this section we outline the steps that will ensure a consistent cloud migration process.
1. Understand what Cloud means for your business
Cloud services are classified into three main types: IaaS, PaaS and SaaS. Understanding which is the best fit for your business will all depend on the needs of your company. Also, consider your company’s infrastructure, all applications, data and systems have to be evaluated. You can determine whether a component is appropriate for cloud migration by being aware of its dependencies and requirements. With AWS consulting services, you will be able to figure out whether a hybrid, public or private cloud will best fit your use case.
2. Choose the right cloud provider
Not all cloud providers are the same, so it’s important to carefully evaluate your options and choose the right provider for your needs. Consider factors such as the provider’s reputation, the services and features they offer, their pricing and cost structure, as well as the level of support and guidance they provide.
3. Figure the differences between cloud environments
Migrating to the cloud, you must grasp the distinctions between the many types of cloud environments (such as public, private, and hybrid clouds) and select the one that best meets your needs. When determining a cloud solution appropriate for your effective data management, it is essential to consider the scale of the company’s data and its storage needs. Also, the performance requirements and the capacity to scale resources in response to shifting workloads are also critical aspects to keep in mind. This awareness will ensure that you can reap the full benefits of cloud computing without sacrificing the security or speed of your operations or overpaying for underused resources.
4. Plan and prepare carefully
Before you begin the actual cloud migration, you need to develop a thorough plan, covering your migration objectives, system architecture, and the possible obstacles and risks. To start moving to the cloud, make sure your system design is as well-suited as possible to the cloud environment you opted for, your resources are under control, and you’ve taken care of your system’s dependencies.
5. Develop a strong security plan
When it comes to cloud migration, security is a significant concern, so it’s necessary to have a comprehensive back-up and continuity plan. This entails safeguards for your data, apps, and infrastructure, as well as policies and procedures for managing and covering the known security risks.
6. Migrate to the cloud
At last, it is time to make the actual transfer of your apps, data, and other resources from on-premises to the cloud. There are different approaches to how you can perform the migration process, based on the business needs and objectives set forth at the preparation stages:
- Lift and Shift: With no need to make significant changes in the underlying architecture, this strategy entails shifting your apps and data from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud.
- Rehosting: Very similar to the lift and shift approach, you will be able to rehost your applications and data to the cloud, yet, there will be minimal changes.
- Replatforming: Your applications are subject to more substantial changes, such as switching to a new platform or updating your apps by using cloud-native features.
- Refactoring: If you want to start fresh and make significant changes to your applications to fully leverage the capabilities of the cloud platform, this is the approach for your company.
7. Monitor and optimize performance
Following the completion of your transfer, it is essential to monitor and optimize the performance of your cloud-based apps and infrastructure. This includes monitoring critical metrics such as uptime, response times, and resource utilization. Consider having a team that will work on the testing process to ensure that the migration has been successful. In addition, you can work on making necessary adjustments for a smoother performance.
Read our article Cloud Migration Checklist: 6 Steps to Successful Cloud Migration to find out even more details on cloud migration.
How Much Money Can Cloud Computing Save?
One of the benefits of using cloud computing is the potential for cost savings. On average, companies save 20% of their infrastructure costs and up to 15% of their support costs by moving to the cloud. These savings can come from a variety of factors, such as hardware elimination, maintenance costs, reduced energy consumption, and the ability to scale resources up or down as needed. Using the cloud can improve the working environment, making it more flexible and efficient. The financial benefits of moving from on premise to the cloud can be significant, although the specific savings will depend on the individual business and its specific needs.
How Do Vendors Calculate Cloud Costs?
Cloud service providers use a variety of factors to determine how much to charge customers for their services. When wanting to calculate cloud costs, you will pay the price depending on your requirements. Some of the most important factors will include networking, computing, and storage costs.
- Networking expenses: In order to provide clients with dependable and efficient service, a vendor must consider the cost of maintaining and upgrading the network. This covers hardware costs such as routers and switches, as well as labor and maintenance. The vendor must also consider the cost of bandwidth as well as other factors that affect network performance.
- Storage costs: The vendor must consider the cost of providing storage for customer data, including the cost of purchasing and maintaining storage hardware, as well as the cost of electricity and other resources needed to keep the data safe and accessible. The vendor must also consider the cost of data transfer and other factors that affect the performance of the storage system.
- Computing costs: The provider must consider the cost of providing computing power to customers, including the cost of purchasing and maintaining hardware, such as servers and CPUs. The provider must also consider the cost of licensing and other factors that affect the performance of the computing system.
Tips to Save Costs
Cloud computing has evolved and will continue increasing due to day by day advancements in the tech sector. The market for cloud computing was worth $545.8 billion in 2022 and is projected to soar to a mind-boggling $1,240.9 billion by 2024, rising at a CAGR of 17.9%.
A survey also reveals End-Users’ projected spending on public cloud services over the past five years. BPaaS, PaaS, SaaS, IaaS, and DaaS are just a few examples of the services that fall under the general category of cloud computing services. Market value increased significantly between 2020 and 2022, rising from $270,033 to $397,496 with a 47.2 increase in growth.
But what about cost savings? According to Gitnux, over 90% of companies use cloud computing services which leads to an annual cost savings of at least 20% on infrastructure costs.
In 2021, businesses acknowledged the costs-saving potential of cloud-based services, leading to a 25% allocation of IT budgets towards these services. The proportion of cloud data center workloads has also significantly increased from 41% to 94%, enabling businesses to continue growing while enjoying cost savings. Additionally, cloud technology offers the opportunity to reduce energy consumption costs by 30-60%.
However, it is crucial to understand how to save on cloud computing expenses. Therefore, we will provide you with some valuable tips to optimize your business and save money.
1. Reduce the cost of downtime
It is no secret that IT companies face two types of challenges in the technological environment. Regardless of which one is in effect, the results have a negative impact provoking financial losses and decreased productivity. While it also affects the overall reputation of the organization.
- The disturbance in the operations caused by planned downtime.
- The recovery of data in situations of unexpected downtime.
Surveys prove that tech outages haven’t really changed. In the past three years, 80% of data center administrators and operators have seen some kind of outage, or downtime according to uptime’s Data Resiliency Survey.
The cost of downtime can be alarming. It may depend from business to business, but a survey has answered that respondents present downtime costs that vary from $1.5 to $5.6 million.
A transfer to the cloud would therefore be much more advantageous when this is taken into account. It is wonderful since cloud companies usually have a number of data centers scattered throughout multiple regions, offering regional redundancy and further reducing the likelihood of outage. Functions like load balancing, data replication, and failover techniques are advantageous if you choose the cloud.
2. Reduce the cost of operations
on-premises servers cost far more than other kinds of computer gear. They are thought to cost between $1,000 and $2,500 on average, yet,these aren’t set rates, and they could increase if you need more powerful servers.
Using on-premises comes with risks for your company. Even having your own IT department, it may not be enough to deal with the internal tasks. For example, SQL Server Database Administrators. The risks present include:
- Performance issues
- Database corruption
- Disruptions to business
In general terms, server costs or the support of servers requires routine maintenance and physical replacement that doesn’t last a while. This means that companies are losing $34 bn per year in unused enterprise software. This includes a waste percentage of 30% of applications that go unused and another 8% are barely used.
So, if you’re looking to cut operational costs you can look into cloud computing services. In fact, it is a lifesaver for your company, especially if you apply common strategies that you can implement to achieve goals for your company that include saving money.
- Automatization
- Outsourcing
- Efficient use of technology
- Continuous improvement
3. Reduce environmental costs
Technology may also have an impact in nature believe it or not. Managing on-premises data stores can be harmful to the environment. We work to help you avoid this problem by providing you cloud computing services.
One-premise infrastructure has direct and indirect costs that will most likely impact your business and the future outcomes of your projects. According to statistics, a quality physical server can cost from $5,000 to $ 15,000. Don’t forget that there are other overlooked expenses that affect you.
- Automatic software updates
- Low costs on hardware
- Flexibility
- Disaster recovery
- Improved partnership
- Unlimited workspace
- Security
- Competitive advantage
- Environmental friendly
A Comparison of Prices From the Major Vendors – AWS vs. Azure vs. GCP

Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are three of the biggest players in the cloud computing market, offering a range of services and pricing models to suit the needs of different customers.
When it comes to pricing, AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure all offer a pay-as-you-go model, where customers only pay for the services they use. This can be an attractive option for businesses that want to avoid the upfront costs of purchasing and maintaining their own hardware and software.
AWS offers a range of pricing options, including the EC2 On-Demand Instances model, where customers pay a fixed hourly rate for each instance they use. Customers can also choose to pay a lower rate for EC2 Reserved Instances, which requires them to commit to using a certain amount of computing power for a one- or three-year term. AWS also offers a Spot Instances model, where customers bid for unused computing capacity at a discounted rate.
Google Cloud also offers a pay-as-you-go model, with prices based on the type and amount of resources used. Customers can also save money by committing to using a certain amount of resources for a one- or three-year term through the Committed Use Discounts program. Google also offers a Sustained Use Discount, which provides automatic discounts for customers that use a consistent level of computing power over a long period of time.
Microsoft Azure offers a pay-as-you-go model, with prices based on the type and amount of resources used. Customers can also save money by committing to using a certain amount of resources for a one- or three-year term through the Azure Reservations program. Azure also offers an Azure Hybrid Benefit, which allows customers to use their existing on-premises licenses to save on cloud costs.
In addition to the pay-as-you-go model, all three vendors offer a range of additional pricing options and discounts. For example, AWS offers discounts for volume purchasing and long-term contracts, as well as discounts for users of certain services, such as AWS Lambda and AWS Fargate. Google Cloud offers discounts for volume purchasing and sustained use, as well as discounts for users of certain services, such as Google BigQuery and Google Kubernetes Engine. Microsoft Azure offers discounts for volume purchasing and long-term contracts, as well as discounts for users of certain services, such as Azure Kubernetes Service and Azure Dev.
Summing Up
Although moving from on-premise to the cloud can become a challenge, it pays off in the long run. It goes without saying that it is dependable, versatile, and convenient. Firms may access data from anywhere at any time thanks to the cloud. It is critical to consider the benefits of moving from on-premise to the cloud, as well as how to begin the process and more detailed information on the cost of the shift.
If you have additional questions as to why companies are moving to the cloud or want to learn more about cloud migration services or cloud-native development, please contact our team by filling out the form below.
FAQ
What are the benefits of moving from on-premise to the cloud?
There is a vast variety of reasons to transition from on premise to the cloud among those with this list you can see why moving to the cloud is worth it:
- Security
- Cost efficiency
- Monitoring and management
- Staff management
- Scalability
- Agility
What is cloud computing?
The act of storing, managing, and processing data on a network of remote servers housed on the internet as opposed to local server or personal computers is what we know as cloud computing.
What are the costs involved in migrating to the cloud?
The cost of migrating to the cloud depends on the size and scope of the project. Additionally, the cost of migrating may depend on each of the cloud platforms available in the market.
How long does it take to migrate to the cloud?
The time for cloud migration depends on a number of factors like the size of the project, the cloud platform it is being transferred to and the size of the team. However, it is possible to come up with an estimated time that can go from two months up to half a year, depending on the complexity of the migration.
How do I choose the right cloud provider for my business?
When having to decide which cloud provider to choose, an in-depth analysis and assessment of the providers is necessary. Yet it is also essential to follow the required expectations to take into consideration features, pricing and other factors that may affect your decision and choice.