AI in Supply Chain and Logistics: Transforming Efficiency and Accuracy

Contents
To support the dynamics of the modern Retail market, to facilitate advancements in Manufacturing, today’s supply chain and logistics industry is in constant search for improvement in its efficiency, adaptability and also precision. The needs and demands of customers are varied and the methods to satisfy them are developing and becoming more and more complex.
However, there are a number of tools and technologies that make it possible to facilitate any complex logistics process. AI (artificial intelligence) is one of those. This transformative technology allows companies to face the demands and challenges of the industry without additional burden on the human employees. It is no secret that the integration of AI in business processes is a path towards growth and development for small and large companies alike. AI is capable of many crucial operations, including performing information analysis (data analysis), detecting data patterns in real time and even making decisions, thus allowing for the optimization of inventories, route planning, contact with suppliers and of course, reaching automation. Adopting AI is becoming more and more essential.
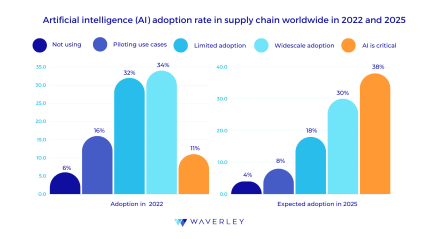
In this article we’ll share the gist about AI in this industry, but let’s start with this graph that shows the increase in AI implementations from 2022 to 2025, by statista:
Understanding Artificial Intelligence in supply Chain and Logistics
For further context, we should mention that Artificial Intelligence refers to a machine simulating human intelligence through detailed and structured processes. For supply and logistics, AI works with a list of technologies to optimize and automate processes as well as decision-making. Furthermore, the application of AI in this industry encompasses a number of supply chain functions, such as purchasing, inventory control, shipping, and customer support.
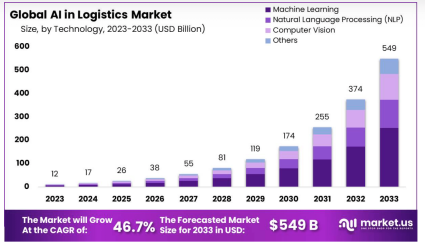
The global market for AI in logistics is expanding quickly as more logistics providers, e-commerce firms, and retailers come to understand the transformative potential of this technology as displayed in this statistics provided by market.us:
Here are some of the areas of AI and Data Science that are currently being utilized to streamline the logistics and supply chain industry:
- Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning algorithms, a subfield of artificial intelligence, enable systems to learn from data and improve over time without the need for explicit programming. Through the analysis of historical data, supply chain management employs machine learning algorithms to estimate demand, optimize inventory levels, and enhance supply chain visibility. For example, ML models can forecast demand trends, allowing companies to adjust their procurement strategies and reduce the risk of overstocks or stockouts.
- Deep Learning: Deep learning is a kind of machine learning that uses neural networks with several layers to model complex patterns in data. This technology is very helpful for tasks involving image identification and natural language processing. Deep learning can be applied to logistics to improve customer experience using chatbots that can understand and respond to natural language queries, automate warehouse quality control, and optimize routes by tracking traffic patterns.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP enables systems to understand and interpret human language. In the supply chain and logistics sector, natural language processing (NLP) can be used to handle information from emails or reports, examine client feedback, and use chatbots to automate customer support and other communications.. By understanding natural language, artificial intelligence (AI) systems may be better able to respond to client questions, coordinate supplier interactions, and extract valuable information from textual data.
- Robotics: Robots are used to perform tasks that are normally entrusted to people. Since robots facilitate delivery and distribution, they is crucial to global supply chains and transportation. Picking up, and sorting are examples of repetitive tasks that robotic arms and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) may perform. This increases operational efficiency and reduces human error. Additionally, robotics increases safety because it can function in hazardous environments and carry out risky activities.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Even if it doesn’t usually fall under AI, Internet of Things technology helps AI by providing real-time data through networked sensors and devices. IoT devices track the position and conditions of things, check the functioning of equipment, and offer real-time data that algorithms can utilize to make supply chain management choices. It also ensures the quality of the supply chain, forecasts equipment maintenance needs, and optimizes transportation routes.
Key Benefits of AI Supply chain and Logistics
The advantages that AI offers to this industry are notable and many. We can summarize them as: AI improves overall performance. In any case, here is a list of the significant improvements:
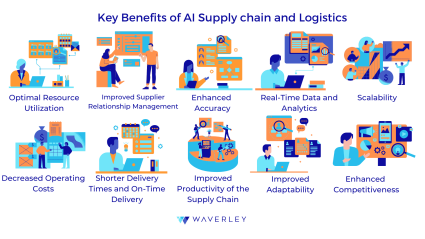
- Optimal Resource Utilization: AI facilitates the best possible utilization of resources, including workers, transportation equipment, and warehousing space. Artificial Intelligence (AI) can suggest changes to resource allocation, ensuring that assets are used efficiently, and reduce waste, by evaluating consumption patterns and operational data.
- Improved Supplier Relationship Management: AI helps to improve supplier relationship management by evaluating data about performance, recognizing possible hazards, and streamlining purchase tactics. Companies can take initiatives to keep a solid supply base by using analytical tools for anticipating quality concerns or delays in supply.
- Enhanced Accuracy: When it comes to processing and interpreting vast amounts of data, artificial intelligence is highly precise. With this ability, delivery of orders, control of inventory, and projections of demand will all be more accurate. By reducing human errors and improving data quality, artificial intelligence (AI) assists organizations in maintaining the ideal amount of stock and minimizing surpluses or overstock situations.
- Real-Time Data and Analytics: Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables real-time supply chain data monitoring and analytics. Companies instantly receive real-time information such as tracking deliveries, estimating delays, and assessing supplier performance, by leveraging advanced analytics and predictive models. Supply chain management’s real-time visibility could help logistics companies respond and act more swiftly in case of delivery issues that may impact end customers.
- Scalability: Systems driven by AI are incredibly scalable, enabling companies to adjust to shifting needs without having to invest as much in additional staff. AI can effectively handle growing data volumes and operational complexity as businesses develop and expand, ensuring that procedures stay efficient and productive.
- Decreased Operating Costs: Artificial Intelligence minimizes the demand for human involvement and labor expenses by automating monotonous daily processes. Tasks like data input, billing, and tracking of supplies, for instance, can be handled by automation of robotic procedures (RPA), which lowers operating costs and frees up human resources for more strategically important work.
- Shorter Delivery Times and On-Time Delivery: AI improves logistics scheduling and optimizing routes, resulting in more predictable and streamlined delivery times. Modern algorithms are able to identify the best routes for delivery by analyzing the climate, travel patterns, and more. This increases the number of on-time deliveries and boosts client happiness.
- Improved Productivity of the Supply Chain: Robotics and automation, two AI-powered technologies, boost efficiency by optimizing logistics and storage operations. Massive production operations like organizing and packaging, can be completed more quickly and accurately by automated equipment, which increases the effectiveness of the supply chain as a whole.
- Improved Adaptability: Artificial intelligence systems possess the ability to promptly adjust to modifications in the marketplace, supply disruptions, or variations in need. Real-time forecast and inventory level adjustments based on fresh data are possible with machine learning models, giving companies the flexibility to quickly address unforeseen obstacles and preserve business continuity.
- Enhanced Competitiveness: Businesses that use AI to their advantage can improve their client service and efficiency in operations and obtain a competitive edge. Especially if they choose and maintain an effective AI strategy for business. So, companies will be able to distinguish themselves from competitors, provide better products and services, and react to consumer changes more efficiently thanks to AI-driven insights and improvements.
AI Application Cases in Supply Chain and Logistics
In the following table we show you the transformative capacity that AI presents in many aspects of the supply chain and logistics in different industries:
| Application Area | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Supply Chain Optimization | To improve procedures like shipping, manufacturing scheduling, and buying, artificial intelligence (AI) models examine information collected from several supply chain nodes. In order to cut expenses and boost productivity, this may involve optimizing the supplier selection process, figuring out the best order numbers, and controlling delivery times. |
| 2. Transportation Management | By examining real-time traffic statistics, meteorological data, and other factors, AI systems enhance travel paths, cut emissions, and speed up shipments. To effectively match drivers and passengers and optimize routes for many pickups and drop-offs, ride-sharing businesses, for example, use artificial intelligence. |
| 3. Demand Forecasting | With a high degree of precision, demand forecasting models driven by artificial intelligence help businesses modify their manufacturing and stock ratios. This is especially helpful for the retail sector, since inventory management and sales tactics can be greatly impacted by a grasp of customer patterns. |
| 4. AI Recommendations for Equipment Maintenance | Artificial intelligence (AI)-powered maintenance plans can identify when hardware is likely to break, allowing businesses to schedule repair in advance. This lowers maintenance expenses and delay, particularly in sectors like manufacturing where machinery uptime is crucial. |
| 5. AI-Driven Inventory Management | In order to improve stock levels, artificial intelligence (AI) systems analyze sales data, seasonality, and market dynamics. This lowers storage expenses and guarantees product availability, especially in industries like e-commerce and healthcare. |
| 6. Dynamic Pricing and Offers | To maximize price strategies, AI algorithms examine rival costs, market trends, and buyer habits. Shops and e-commerce businesses can provide specific offers to draw customers and optimize income with the help of this dynamic pricing technique. |
| 7. Automation of Warehouse Operations | AI-powered robotics and automation systems in warehousing help to optimize operations including selection, packaging, shipping, and categorizing. Robotic arms and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) that employ artificial intelligence (AI) have the capability to do intricate jobs, hence enhancing customer service efficiency and precision. |
| 8. Supply Chain Risk Management | To anticipate and lessen supply chain interruptions, artificial intelligence (AI) systems can examine geopolitical events, natural catastrophes, and other risk variables. For sectors that depend on intricate, international supply chains, like electronics and the automotive industry, this skill is crucial. |
| 9. Impact on ecological health and sustainability | AI can streamline logistics processes to lower carbon emissions and advance sustainability. For example, by precisely predicting demand and controlling perishable commodities, artificial intelligence (AI) can assist the food and beverage industry in streamlining delivery routes and cutting down on food waste. |
| 10. Individualized Customer Service | By responding to questions, keeping track of requests, and making suggestions for goods, AI chatbots and virtual assistants offer individualized customer service. By making customized recommendations, these AI applications improve user experience and boost sales in the fashion and consumer goods sectors. |
Best Practices for Implementing AI in Supply chain and Logistics
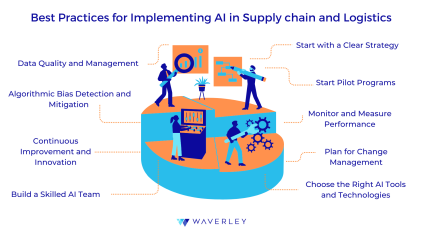
1. Start with a Clear Strategy
- Set Objectives: Specify quantifiable goals for integrating AI into your logistics and supply chain processes. This could entail cutting expenses, expediting deliveries, raising accuracy, or boosting client satisfaction.
- Audit Value Creation: Evaluate your supply chain’s existing condition and pinpoint the areas where AI can be most useful. This entails assessing current procedures, spotting inefficiencies, and figuring out possible areas for automation and improvement.
- Set Clear Priorities: Using the audit results as a guide, rank AI projects according to their potential ROI and alignment with your company’s objectives. Examine elements including complexity, viability, and effect on the supply chain as a whole.
2. Build a Skilled AI Team
- Hire an Expert Team: Put together a group of professionals with a range of expertise, such as supply chain analysts, data scientists, machine learning development and IT experts. The creation, application, and administration of AI solutions will fall within the purview of this group.
- Foster Collaboration: Promote cooperation across the AI team and other divisions, including customer service, operations, and procurement. The smooth integration of AI technologies into current operations and their alignment with business goals are guaranteed by this cross-functional approach. A good option to have a functional team without the burden of recruitment and onboarding is to consider hiring nearshore software development teams.
3. Choose the Right AI Tools and Technologies
- Select correct tools: Choose the AI platforms and tools that best fit the goals and requirements of your company. Take into account elements like compliance with current systems, ease of insertion, and scalability. Consider factors like experience, customer feedback, and support provided while evaluating suppliers and solutions.
4. Start Pilot Programs
- Start with Pilot Projects: For testing AI solutions in practical settings, start small-scale pilot projects. While scaling up, this enables you to verify the technology, assess its effects, and find any possible problems.
- Scale: Apply AI solutions throughout the company in accordance with the outcomes of pilot projects. Create a scaling plan that outlines important dates, resource allocation, and goals.
5. Data Quality and Management
- Gather Information: Compile information from the supply chain’s many sources, such as sales, stock, shipping, and client reviews. Make certain that the data is gathered in an organized and standardized manner.
- Assure Data Quality: for validity, fullness, and dependability, put data quality management procedures into place. This covers procedures for data normalization, validation, and cleansing.
- Data Integration from Various Sources: Combine data into a consolidated data pool or store by integrating data from various sources. This facilitates advanced analytics and AI applications and allows for a comprehensive picture of the supply chain.
6. Algorithmic Bias Detection and Mitigation
- Find Possible Obstacles: Examine AI models and algorithms for any potential obstacles in the information or the procedures used to make decisions. Those problems can result from data representation, model beliefs, or past data.
- Put Offset Strategies into Practice: Create plans to lessen errors that have been found, such as redistributing training data, changing model variables, or putting in place fairness limits. Make sure AI systems are built with equitable treatment of all data and judgments in mind.
- Constant Tracking: Keep an eye out for any new or developing faults in AI systems. To guarantee accuracy and fairness, audit AI models frequently and change them as necessary. This constant watchfulness contributes to the integrity of decisions made by AI.
7. Monitor and Measure Performance
- Define KPIs: To gauge the effectiveness of AI projects, define key performance indicators (KPIs). Metrics like cost savings, delivery accuracy, customer happiness, and replacement of stock are examples of KPIs.
- Conduct Regular Reviews: Evaluate the effectiveness of AI solutions by conducting regular evaluations. To maximize AI applications, analyze KPI data, pinpoint areas for development, and make data-driven choices.
8. Plan for Change Management
- Create a Strategy for the Management: Create a change management strategy to aid in the company’s implementation of AI technologies. This entails educating staff members, outlining the advantages of AI, and handling any potential opposition to change.
9. Continuous Improvement and Innovation
- Always Innovate: Encourage a culture of innovation and ongoing development. Motivate the AI team to investigate emerging technologies, approaches, and applications. Update AI systems often to take advantage of the newest developments and industry best practices.
Implementation Challenges
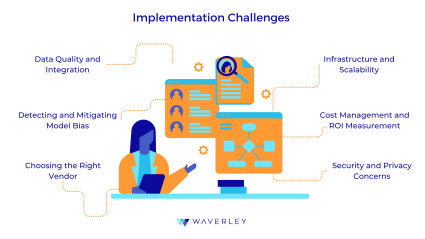
- Data Quality and Integration: Working with insufficient, wrong, or missing data poses a number of key issues for supply chain and logistics AI implementation, since this might result in faulty algorithms and ideas. Furthermore, it might be difficult and time-consuming to integrate data from several sources. Companies should have strong data governance and management procedures in place, together with comprehensive procedures for data cleaning, validation, and standardization, to solve these problems. While putting in a single data platform guarantees effective data management and storage, ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) solutions can provide smooth data integration.
- Detecting and Mitigating Model Bias: False or incorrect results may result from AI algorithms unintentionally amplifying or perpetuating beliefs found in training data. It is essential to routinely audit and test AI models for bias in order to address this concern. It can be lessened in training by using relevant and varied datasets. To further guarantee fair model performance, strategies including reweighting, data augmentation, and fairness constraints can be put into practice. To preserve accountability and trust, transparency in the model-development and decision-making processes is also crucial.
- Choosing the Right Vendor: It can be difficult to choose the right AI supplier because there are so many possibilities accessible, and there are differences in terms of AI software development services regarding quality and competence. Companies should evaluate suppliers based on their technological capabilities, experience, and customer feedback in order to perform extensive due diligence and traverse this complexity. To help make an informed decision, pilot projects with the vendors that made the short list might offer insightful information about how well they fit the demands of the company.
- Infrastructure and Scalability: As artificial intelligence applications grow, there is a greater need for servers, memory, and computational resources, which creates scalability issues. In order to get around this, businesses need to invest in infrastructures and scalable cloud-based solutions that can manage increasing amounts of data and computing demands. Hybrid cloud solutions are flexible and can facilitate scalable AI deployment by integrating on-premises and cloud resources. A strong IT infrastructure is necessary to provide smooth growth and meet the growing requirements of AI systems.
- Cost Management and ROI Measurement: Cost management as well as return on investment (ROI) analysis are important concerns since AI initiatives can necessitate significant expenditures in infrastructure, personnel, and technology. Companies should create a thorough business case for AI investments that details expected costs and benefits in order to handle these factors efficiently. Pilot projects are a useful tool for confirming the viability and possible return on investment of AI technologies. Ensuring that investments are maximized and in line with business objectives requires regular monitoring of project costs and benefits in addition to strategic modifications.
- Security and Privacy Concerns: Data security and privacy are challenges raised by the fact that AI systems frequently need access to sensitive data. Companies should put strong cybersecurity measures in place, like encoding, access limits, and frequent security audits, to reduce these risks. It is also important to make sure that data privacy laws like the CCPA and GDPR are followed. By balancing information use and security, methods such as shared learning and differential privacy can improve data privacy without compromising the accuracy of AI models.
Best Examples
- Amazon: When it comes to using AI to streamline its logistics and supply chain, Amazon has led the way. As a way to drastically cut down on order processing times, the company automates the picking and packing process in its fulfillment facilities using AI-driven robots. Furthermore, in order to guarantee efficient storage and on-time delivery, Amazon’s AI algorithms forecast product demand and optimize delivery routes. One distinctive feature of Amazon’s AI deployment is “anticipatory shipping,” which reduces delivery times by anticipating client requests and distributing products to local hubs before the purchase is even placed.
- Walmart: To cut waste and simplify inventory management, Walmart uses artificial intelligence. The business anticipates demand for goods using machine learning algorithms, which improves selling accuracy and lowers the risk of overstocking or stockouts. To try to improve its supply chain processes, Walmart also uses AI-powered chatbots for customer support and real-time data analytics. Walmart’s innovative approach involves leveraging blockchain technology in tandem with artificial intelligence to improve food tracking and safety. This facilitates the prompt identification of contaminated products.
- Maersk: As a pioneer in the shipping sector, Maersk uses AI to enhance fuel economy and optimize transportation routes. With the goal to improve speed and route planning and minimize fuel use and emissions, the company’s AI-driven systems analyze data on weather, ocean currents, and port congestion. Additionally, Maersk has created “Captain Peter,” an AI-powered virtual assistant that gives ship captains access to real-time information and insights to help them make wise decisions. Maersk’s use of AI to improve cybersecurity and shield its shipping operations from online threats is a great idea.
- DHL: DHL has integrated AI into a number of key supply chain processes, such as predictive analytics and automated warehouses. Robots and drones with AI capabilities are used by the corporation for inventory management and in-the-moment warehouse operations monitoring. Additionally, DHL uses machine learning algorithms to examine client information and enhance shipping routes. DHL’s “Resilience360” platform is an innovative project that employs artificial intelligence (AI) to evaluate supply chain risks, including natural disasters and political unrest, enabling the corporation to proactively handle possible disruptions.
Successful metrics
The following key performance indicators (KPIs) can be monitored by enterprises to assess the effectiveness of AI implementations in supply chain and logistics:
- Operational Efficiency: Measures that show gains in effectiveness and efficiency include the automation success percentage, shipping time, and orders processing time.
- Cost Savings: Assess operational cost savings, including lower labor and transportation fees, as well as improved fuel efficiency.
- Inventory management: To evaluate the precision of demand forecasts and manage inventories, and monitor the stock percentage of turnover and stockout rate.
- Customer Satisfaction: To measure client approval and loyalty, use Net Promoter Score (NPS) and Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT).
- Resilience in Supply Chain: Evaluate how well risk-reduction tactics work and how quickly supply chain disruptions can be addressed.
- QA: To guarantee high-quality operations, keep an eye on error rates and the precision of demand predictions.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Determine the total value created by comparing the financial gains of artificial intelligence (AI) with its expenses.
AI in Logistic: Conclusion
AI has revolutionary advantages for supply chains and logistics, including increased accuracy, cost savings, and efficiency. Artificial intelligence (AI) helps organizations increase customer happiness and streamline operations by automating repetitive jobs, organizing inventory management, and forecasting demand. Projection of demand, inventory optimization, transportation management, and predictive maintenance are some of the key uses. These technologies increase competition and adaptability by enabling real-time data analysis, cutting operating costs, and speeding up delivery times. Companies that use AI-powered solutions might have a big advantage in the competitive market of today. Companies may boost innovation and growth while improving operational efficiency by investigating and implementing AI technologies.
We advise businesses to assess their current procedures and look for ways to integrate AI in order to start the process of digital transformation. To fully realize the potential of AI in your supply chain and logistics operations, work with us to develop a competent AI team, begin with test projects, and select the appropriate technologies. AI is driving the future; embrace it now to keep up with industry innovation!
Discover how AI can optimize your supply chain and logistics smoothly.
Transform logistics with AI-powered solutions
FAQ
What is AI in supply chain and logistics?
Using artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to improve supply chain management in a variety of ways, including demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and work automation, is known as AI in supply chain and logistics AI. AI facilitates data-driven decision-making and raises overall operational effectiveness.
How can AI improve supply chain efficiency?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) enhances supply chain efficiency through the automation of repetitive processes, optimization of inventory levels, improved route planning, and more accurate demand prediction. This results in lower expenses, quicker delivery, and better operational performance all around.
How do I get started with implementing AI in my supply chain?
Establishing your objectives and pinpointing important areas for development is the first step in implementing AI. Start with trial projects to evaluate solutions, do a data audit, and select the right AI technologies. assemble knowledgeable staff, guarantee data quality, and progressively expand depending on the outcomes.
What is the role of AI in logistics and supply chain?
AI plays a crucial role in logistics and supply chain by optimizing processes such as demand forecasting, inventory management, transportation planning, and risk assessment. It enhances decision-making, reduces costs, and improves efficiency throughout the supply chain.