How to Use Artificial Intelligence in Manufacturing

Contents
Artificial Intelligence (AI) will bring a new era of efficiency, accuracy, and creativity in manufacturing. Manufacturers may streamline procedures, cut expenses, and enhance product quality by utilizing AI. Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies are finding their way into many manufacturing phases, from supply chain management and design to maintenance and quality control. These include generative AI for machine learning, robots, computer vision, and predictive analytics, which helps businesses remain competitive in a rapidly evolving market. This shift aims to improve human capacities and create smarter, more responsive industrial settings rather than just substituting humans with machines.
Let’s examine how AI is used in manufacturing and what its role is going to be in contemporary manufacturing. In this article we’re striving to look at the many AI technology platforms in use and offer a thorough examination of particular uses and practical examples. Along with outlining how to implement AI in your business and the procedures for putting AI solutions into practice in the industrial sector, we’ll also highlight Waverley’s practical experience in providing tailored AI solutions that promote industry change in the hopes that other businesses will find it useful and applicable to their technology transformation initiatives.
The Role of AI in Manufacturing
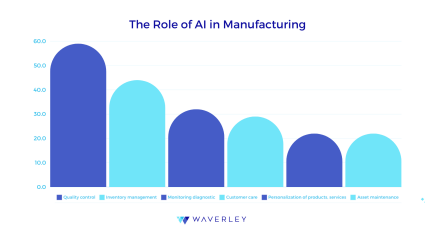
AI is a term used to describe how technology, especially computer systems, can simulate human intelligence processes. Learning (the process of acquiring knowledge and applying rules to it), reasoning (using rules to arrive at approximations or conclusions), and self-correction are some examples of these processes. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in the manufacturing industry is becoming a critical component of the modernization processes and systems, enabling them to be smarter, more efficient, and highly responsive to shifting market demands. Also, quality control is ranked as the most significant AI use case in the manufacturing sector by 59% of respondents according to Statista. Smart camera inspection, cost reduction, and manufacturing standardization are only a few of the ways AI improves quality control.
Applying AI to improve Manufacturing processes is one of the main components of Industry 4.0, or the fourth industrial revolution, which is defined by the combination of digital technologies, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things. Industry 4.0 trends include predictive maintenance, which employs machine learning algorithms to forecast equipment problems before they occur, which leads to decreasing downtime and maintenance costs. In addition, we see the rise of so called “smart factories”, where AI-driven systems monitor and improve production processes in real time. Furthermore, the most recent developments in artificial intelligence (AI) for manufacturing companies include the application of cooperative robots (cobots), sophisticated robotics for automation, and AI-enabled supply chain management to optimize processes and boost productivity. These developments highlight AI’s critical role in building manufacturing ecosystems that are more responsive, resilient, and agile.
The Types of AI Technologies Used in Manufacturing
The manufacturing industry uses a range of AI technologies, each with special powers to improve and optimize various parts of industrial processes. These technologies include, among others, chatbots with artificial intelligence, computer vision, robotics, predictive analytics, and machine learning. Let’s give a bit more context below:
- Machine Learning (ML): Machine learning refers to the use of techniques that let systems learn from data and get better over time without requiring explicit programming. By examining historical data to forecast equipment failures, machine learning (ML) in manufacturing helps to reduce maintenance costs and downtime. By spotting trends and providing data-driven suggestions, it also enhances production procedures. Collaborating with an ML development company can streamline the implementation process, ensuring that tailored machine-learning solutions are effectively integrated into manufacturing operations.
- Predictive analytics: This method of analyzing past data and forecasting future events makes use of statistical algorithms and machine learning approaches. It is employed in manufacturing to forecast demand, maximize inventory levels, and enhance the effectiveness of the supply chain. Manufacturers can anticipate market changes and match client requests by using predictive analytics to inform their actions.
- Computer Vision:Computer vision is the application of AI to the interpretation and processing of real-world visual data. It is extensively utilized in manufacturing for fault detection and quality control. Only high-quality products will reach the market thanks to computer vision systems’ ability to precisely detect flaws or irregularities in products being inspected in real-time on production lines.
- AI Chatbots: AI chatbots are used in the manufacturing ecosystem to improve communication and expedite processes. These chatbots may answer supplier questions, help with customer support, and give real-time manufacturing status updates. By means of automating normal communication chores and giving prompt answers to frequently asked questions, they increase manufacturing efficiency and productivity.
- Robotics: AI is used in robotics to improve automation and accuracy in the manufacturing sector. Robots driven by artificial intelligence (AI) are capable of carrying out intricate activities like welding, painting, and product assembly with exceptional accuracy and consistency. Cobots, or collaborative robots, support human laborers by enhancing their abilities and boosting efficiency and security as a whole.
- NLP: Natural Language Processing makes it possible for computers to comprehend and react to human language. NLP is used in manufacturing to examine unstructured data from technical documentation, customer reviews, and maintenance logs in order to obtain knowledge and enhance decision-making procedures. Utilizing Python for AI, developers can create powerful NLP models that effectively process and analyze large volumes of text data, thereby improving the accuracy and efficiency of these systems.
- Generative Design: Based on predetermined limitations and objectives, generative design employs AI algorithms to explore a broad range of design possibilities. This technology facilitates the development of creative and efficient product development processes by assisting in the creation of novel product designs that are optimized for cost, performance, and manufacturability.
These artificial intelligence (AI) technologies each have unique benefits for the manufacturing industry, boosting productivity, creativity, and efficiency. Manufacturers may design manufacturing systems that are more intelligent, responsive, and agile by integrating these cutting-edge technologies.
How is AI Used in the Manufacturing Industry?
In the manufacturing sector, artificial intelligence (AI) is a game-changer, bringing about significant gains in productivity, efficiency, and creativity. Manufacturers may lower costs, improve product quality, expedite processes, and maintain competitiveness through the use of AI technologies. This section delves deeper into certain uses of AI in the manufacturing industry, including numerous studies and research projects that demonstrate the technology’s significance.
- Predictive Maintenance
By analyzing data from sensors built into machinery, predictive maintenance employs artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to forecast equipment breakdowns before they happen. This strategy increases machine lifespan, lowers maintenance costs, and minimizes downtime. Predictive maintenance can save maintenance costs by 25% and prevent breakdowns by up to 70%, according to a Deloitte study. General Electric (GE), for example, uses AI to track and forecast the maintenance requirements of its industrial equipment, which reduces costs significantly and boosts operational effectiveness. - Quality Control and Defect Detection
AI, especially computer vision, is vital to manufacturing because it plays a key role in quality control and defect detection. AI systems can do real-time product inspections, spotting flaws and guaranteeing superior standards. For example, BMW uses AI-powered quality control systems to find irregularities in their manufacturing lines and make sure that only the best cars get out of the factory. Artificial Intelligence (AI)–based defect detection systems have the potential to greatly increase product quality and decrease waste, according to a study published in the Journal of Manufacturing Processes. - Supply Chain Optimization
Through demand prediction, inventory optimization, and improved logistics, artificial intelligence (AI) improves supply chain management. By properly predicting future demand through the analysis of past data and market patterns, machine learning algorithms allow manufacturers to maintain appropriate inventory levels. Amazon employs artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize its supply chain processes, leading to reduced operating expenses and expedited delivery times. According to research published in the International Journal of Production Economics, supply chain optimization powered by AI can result in notable cost savings and increases in productivity. - Process Optimization and Production Efficiency
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems examine production data to find inefficiencies and suggest fixes that boost output while cutting waste. According to McKinsey, process optimization powered by AI may increase the output by 20%. Artificial intelligence (AI) systems constantly monitor production processes and make real-time parameter adjustments to ensure peak performance. Siemens, for instance, optimizes their production processes using AI to increase productivity and lower energy usage. - Robotics and Automation
Automation, accuracy, and efficiency in manufacturing processes are improved by AI and robotics powered by itself. AI-equipped robots are capable of very accurate and reliable performance of complicated operations like welding, painting, and assembly. Cobots, or collaborative robots, complement human laborers by enhancing their abilities and raising output levels. Businesses such as FANUC greatly increase operating efficiency in production environments by deploying innovative robotic systems. The advantages of AI-powered robotics in boosting production automation are highlighted by research from the fields of robotics and computer-integrated manufacturing. - Energy Management and Sustainability
AI assists producers in optimizing energy use, lowering expenses and negative environmental effects. AI systems track and control energy consumption in real-time, finding areas where energy can be saved. Siemens uses AI to improve factory energy management, fostering cost-effectiveness and sustainability. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based energy management systems can result in large energy savings and lower carbon emissions. - Demand Forecasting and Inventory Optimization
High-accuracy client demand prediction is made possible by machine learning algorithms, which help producers keep the right amount of inventory on hand. This lowers the cost of storage and helps prevent overproduction or stockouts. Walmart, for instance, forecasts demand and optimizes inventory using AI to minimize surplus stock and guarantee that products are available when customers need them. Moldstud highlights how AI may enhance inventory control and demand forecasting accuracy. - Risk Management
Artificial Intelligence evaluates supply chain and production process risks, assisting enterprises in averting such interruptions. Artificial Intelligence (AI) offers practical insights to improve risk management techniques by analyzing data from several sources. A World Economic Forum analysis demonstrates how artificial intelligence (AI) may enhance risk assessment and management in the industrial sector, guaranteeing more robust supply chains. AI solutions allow manufacturers to take proactive measures by anticipating and mitigating risks associated with production delays, supply chain interruptions, and quality difficulties. - Product Design and Innovation
Manufacturers may generate novel goods by experimenting with endless design combinations thanks to AI-powered generative design tools. These instruments aid in the creation of stronger, lighter, and more effective products. Businesses such as Airbus leverage generative ai development in design to produce lightweight, durable, and innovative airplane components. The benefits of artificial intelligence (AI) in augmenting product design and innovation are explored in a paper published in the Journal of Mechanical Design. This allows manufacturers to push the envelope of creativity and efficiency. - Cobots
By helping with jobs that call for strength and accuracy, collaborative robots, or cobots, increase worker safety and productivity while also increasing overall production efficiency. Cobots are made to assist human workers by performing tedious or physically taxing jobs. A case study from Universal Robots demonstrates how cobots can enhance working conditions and boost productivity in manufacturing settings. The benefits of cobots in improving industrial productivity and safety are highlighted in this research by AZORobotics. - Optimize Documentation Processes
By automating the development, administration, and analysis of production-related documents, artificial intelligence (AI) simplifies documentation. This guarantees efficiency, accuracy, and compliance when managing enormous volumes of data. Document management solutions with AI capabilities can extract data, classify documents, and spot patterns—all while requiring a great deal less manual labor. According to the research published in the Journal of Manufacturing Systems, artificial intelligence (AI) can streamline documentation procedures, increasing operational effectiveness and lowering administrative burden.
AI Implementation Process in Manufacturing
Putting AI solutions into practice in manufacturing requires a methodical process that includes several crucial elements. Every stage of the procedure needs to be customized to the unique aims and objectives of the manufacturing enterprise. The general procedures for putting AI solutions into practice are described in this part, emphasizing the significance of meticulous planning, data management, model creation, testing, and deployment.
1. Planning
The establishment of the project’s goals and objectives is the initial stage in integrating AI into manufacturing. This entails being aware of the particular issues that must be resolved as well as the possible advantages of using AI solutions. This phase should involve key stakeholders to guarantee alignment with corporate objectives. A precise plan of action should be created, detailing the project’s objectives, schedule, and necessary resources.
2. Gathering and Preparing Data
The foundation of any AI system is data. Relevant data is gathered during this phase from a variety of sources, including sensors, devices, and old records. The success of AI models is heavily influenced by the quantity and quality of data. Cleaning, standardizing, and formatting the data into an appropriate format for analysis are all part of the preprocessing process. To make sure the data is correct and prepared for model building, this phase is essential.
3. Training and Model Development
Developing and training AI models is the next stage after obtaining the preprocessed data. This entails choosing the right methods and algorithms depending on the particular use case. While unsupervised learning techniques may be employed for anomaly detection, machine learning models, for example, need labeled datasets to learn. Using the gathered data, the models are trained, and their performance is enhanced by modifying certain parameters. The models are iterated until they reach the appropriate degree of precision and dependability.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Industrial Execution Systems (MES) and Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) are two examples of modern industrial systems that require integration with AI technologies. The smooth exchange of data and compatibility between AI applications in manufacturing and other business procedures are guaranteed by this integration. To enable real-time data transmission and decision-making, APIs and middleware technologies are frequently utilized.
5. Validation and Testing
Thorough testing and validation are necessary prior to implementing AI models in a live production setting. In order to assess the models’ correctness and performance, test data is used in this phase. It is important to fix any problems found during testing and adjust the models as necessary. Validation guarantees that the AI solutions fulfill the defined objectives and are prepared for implementation. Stress testing is another step in this process that evaluates the models’ performance in various scenarios.
6. Initiation and Supervisory
AI models are implemented in the production environment after they have been examined and approved. The goal of this step is to ensure that the models perform seamlessly with current systems by incorporating them into the manufacturing workflow. To monitor AI systems’ performance and spot abnormalities or potential improvement areas, it is imperative to conduct ongoing monitoring. In order to keep the models current and functional in light of evolving conditions, regular updates and maintenance are necessary.
Real-World AI in Manufacturing Examples
Here are a few noteworthy top companies using AI in manufacturing cases and illustrations showing how artificial intelligence is being applied in manufacturing settings.
1. Primarily, GE and Predictive Maintenance
In order to enable predictive maintenance on its diverse industrial equipment, General Electric (GE) has integrated AI. To forecast possible breakdowns before they happen, GE analyzes data from sensors integrated into jet engines, turbines, and other gear using AI algorithms and machine learning models. By being proactive, they have decreased downtime, increased equipment longevity, and saved a substantial amount of money. Presumptive maintenance solutions powered by AI, according to GE, have lowered maintenance expenditures by 25% and unexpected downtime by up to 20%.2. BMW and Inspection
Only the best cars are allowed to exit BMW’s assembly lines thanks to the use of AI-powered quality control technologies. Real-time car inspections for flaws and irregularities are conducted by AI systems equipped with computer vision capabilities. These devices have the ability to find even the smallest irregularities that human inspectors could overlook, such as paint flaws or misalignments. As a result, there are now fewer defective cars being delivered to consumers, and BMW’s quality assurance procedures have been enhanced significantly.3. Optimization of Supply Chain and Amazon
Amazon is leading the way in supply chain optimization powered by AI. The company optimizes inventory levels, streamlines transportation, and predicts client demand using machine-learning algorithms. By ensuring on-time delivery and cutting expenses, artificial intelligence (AI) assists Amazon in effectively managing its extensive and intricate supply chain network. Amazon has been able to sustain high service levels and customer happiness thanks in large part to this AI-driven approach.4. Demand Forecasting and Walmart
Walmart leverages AI to improve inventory control and demand predictions. To precisely forecast client demand, machine learning models examine market trends, past sales data, and other variables. Walmart is able to keep stockouts to a minimum and maintain ideal inventory levels as a result, saving money on storage. Walmart has been able to efficiently satisfy consumer needs and maintain excellent levels of service with the help of AI-driven demand forecasting.5. Cobots and Universal Robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are machines designed by Universal Robots that operate alongside humans to increase efficiency and security. These AI-powered cobots help with assembly and material handling, two jobs that need strength and accuracy. Cobots have increased overall production efficiency and made workplaces safer by enhancing human capabilities. Cobots made by Universal Robots are employed in a number of sectors, including industrial manufacturing automotive electronics, and healthcare industries.6. Autonomous Manufacturing with Tesla
Tesla is innovating its autonomous manufacturing by automating different parts of its production processes with artificial intelligence. AI-driven robots and automated systems quickly and precisely complete complicated jobs like welding, painting, and assembling. In order to fulfill the rising demand for its electric vehicles, Tesla has been able to considerably raise production rates and enhance product quality thanks to its AI-powered manufacturing processes.Transforming Manufacturing with Waverley’s Custom AI Solutions
When it comes to providing customized AI solutions with an emphasis on innovation and transformation for the industrial industry, Waverley Software is a leading provider in this area. We provide real-time monitoring and failure prediction for predictive maintenance, automated inspection and defect detection for quality control, and workflow automation and efficiency enhancement for process optimization. We also optimize logistics and demand forecasting to improve supply chain management. For a range of manufacturing requirements, our custom AI development offers solutions that are specifically designed to ensure seamless integration and continuous support. We demonstrate notable improvements in efficiency, quality, and cost savings through innovation showcases and proven client success, enabling manufacturers to become more competitive in an increasingly digitized and automated sector.
Conclusion
AI is transforming manufacturing through increased productivity, creativity, and quality having a significant impact on manufacturing operations, as demonstrated by key applications like quality control, supply chain optimization, robotics and automation, energy management software, and more. Important cost savings, higher productivity, less downtime, and better product quality are all achieved with these AI-driven solutions. It can be used to monitor energy usage, guarantee product quality, optimize processes, and anticipate and prevent equipment breakdowns. Businesses must investigate and capitalize on AI prospects since the manufacturing industry of the future will be intelligent, automated, and AI-driven. That is why manufacturers should begin by determining which parts of their operations could profit from this intelligence in order to stay ahead of the curve.
The time has come to adopt AI and propel your manufacturing company into the future. Examine how AI can revolutionize your business, boost output, and raise the caliber of your output. Get in touch with us right now to find out more about our unique AI solutions created especially for the manufacturing sector.
Enhance efficiency and quality in manufacturing with AI.
FAQ
What are the applications of manufacturing AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) finds multiple applications in the manufacturing sector: for the optimization of production processes, such as supply chain optimization, quality control, predictive maintenance, and production efficiency. In order to anticipate equipment failures, identify flaws, simplify logistics, and boost overall operational efficiency, artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms evaluate data from sensors and machines. For example, computer vision systems improve quality control by instantly spotting faults, while AI-powered predictive maintenance can minimize downtime by anticipating equipment issues before they happen.
Which AI technologies are most frequently used in the manufacturing industry?
AI chatbots, computer vision, robots, machine learning, and predictive analytics are just a few of the technologies used by the manufacturing industry. Demand forecasting and predictive maintenance both make use of machine learning methods. Automation and robotics combine AI to carry out difficult jobs with extreme accuracy. Computer vision systems are utilized for defect detection and quality control, while predictive analytics aids in supply chain optimization. Artificial intelligence chatbots help with customer service and enhance communication in the supply chain.
Is it possible for AI to work with current production systems like MES and ERP?
Indeed, artificial intelligence (AI) may work in unison with current production systems like manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP). Real-time data interchange and improved decision-making are made possible by this integration. Manufacturers can use APIs and middleware solutions to connect AI apps to these systems and use AI insights to optimize inventory control, production scheduling, and overall operational efficiency.
How can AI improve the productivity of manufacturing?
AI improves manufacturing productivity by decreasing downtime, streamlining production procedures, and automating monotonous jobs. AI-driven process optimization, for instance, can locate bottlenecks and suggest changes to enhance production flow. By reducing unanticipated equipment failures, predictive maintenance ensures uninterrupted operations. AI also improves energy management by optimizing energy use, which lowers expenses and helps with environmental initiatives. In general, artificial intelligence (AI) makes manufacturing operations more economical, efficient, and sustainable.
Unlock the full potential of AI in manufacturing